Database
Database is a collection of interrelated data.
- A database is an organized collection of data that can be easily accessed, managed, and updated.
- It stores data in tables, rows, and columns, allowing efficient retrieval and manipulation.
- Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB.
DBMS
DBMS(Database Management System) is software used to create, manage, and organize databases.
- A DBMS is software that manages and controls database operations like storing, retrieving, and updating data.
- It ensures data consistency, security, and integrity while providing an interface for users to interact with the database.
- Examples include MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server. 🚀
What is RDBMS
- RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) - is a DBMS based on the concept of tables (also called relations).
- Data is organized into tables(also known as relations) with rows(records) and columns(attributes).
- E.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server etc.
SQL
SQL is Structured Query Language - used to store, manipulate and retrieve data from RDBMS.
We use SQL for CRUD Operations:
- CREATE - To Create databases, tables, insert tuples etc.
- READ - To read data present int the database.
- UPDATE - Modify already insert data.
- DELETE - Delete database, table or specific data point/tuple/row or multiple rows.
NOTE : SQL keywords are NOT case sensitive. E.g., select is the same as SELECT in SQL.
Create Database
We can use the the following command to create the database.
CREATE DATABASE database_name;
Delete Database
We Can use the DROP command to delete the database.
DROP DATABASE database_name;
Select/Use the Database
We can use the USE command to select db and perform operation.
USE db_name;
SQL vs MySQL
SQL is a language used to perform CRUD operations in Relational DB, while MySQL is a RDBMS that uses SQL.

Creating Table
We can create the table in db using the CREATE TABLE command whole syntax is given below.
CREATE TABLE table_name(
column_name1 datatype constraint;
column_name2 datatype constraint;
column_name3 datatype constraint;
);
SQL Data Types
In SQL, data types define the kind of data that can be stored in a column or variable.
| Datatype | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR | String (0-255), can store characters of fixed length | CHAR(50) |
| VARCHAR | String (0-255), can store characters up to given length | VARCHAR(50) |
| BLOB | String (0-65535), can store binary large object | BLOB(1000) |
| INT | Integer (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647) | INT |
| TINYINT | Integer (-128 to 127) | TINYINT |
| BIGINT | Integer (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807) | BIGINT |
| BIT | Can store x-bit values. x can range from 1 to 64 | BIT(2) |
| FLOAT | Decimal number - with precision to 23 digits | FLOAT |
| DOUBLE | Decimal number - with 24 to 53 digits | DOUBLE |
| BOOLEAN | Boolean values 0 or 1 | BOOLEAN |
| DATE | Date in format of YYYY-MM-DD ranging from 1000-01-01 to 9999-12-31 | DATE |
| TIME | HH:MM:SS | TIME |
| YEAR | Year in 4-digit format ranging from 1901 to 2155 | YEAR |
Note - CHAR is for fixed length & VARCHAR is for variable length strings. Generally, VARCHAR is better as it only occupies necessary memory & works more efficiently.
Signed & Unsigned : We can also use UNSIGNED with datatypes when we only have positive values to add. Eg - UNSIGNED INT
TINYINT UNSIGNED (0 to 255)
TINYINT (-128 to 127)
Types of SQL Commands
- DDL(Database Definition Language): Used to create, alter, delete database objects like tables, indexes, etc. (CREATE, DROP, ALTER, RENAME, TRUNCATE).
- DQL(Database Query Language): Used to retrieve data from databases. (SELECT).
- DML(Database Manipulation Language): Used to modify the database. (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
- DCL(Database Control Language): Used to grant & revoke permissions. (GRANT, REVOKE).
- TCL(Transaction Control Language): Used to manage transactions, (COMMIT, ROLLBACK, START TRANSACTIONS, SAVEPOINT).
DATABASE related Queries
CREATE DATABASE db_name; -- used to create database
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS db_name; -- create database if database not exist of this name.
DROP DATABASE db_name; -- delete database
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS db_name; -- delete database if exists
SHOW DATABASES; -- show all databases
SHOW TABLES; -- used to show all tables in particular database
Table related Queries
Create Tables
We can use the following syntax to create the table or design the scheme of table.
CREATE TABLE table_name(
column_name1 datatype constraint;
column_name2 datatype constraint;
);
Example
CREATE TABLE student(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
age INT NOT NULL
);
Select & View ALL columns
SELECT * FROM table_name; -- display whole table
Insert
INSERT INTO table_name
(colname1, colname2);
VALUES
(col1_v1, col2_v1),
(col1_v2, col2_v2);
Keys
Primary Key
It is a column (or set of columns) in a table that uniquely identifies each row. (a unique id). There is only 1 Primary Key and it should not be NOT null
Foreign Key
A foreign key is a column (or set of columns) in a table that refers to the primary key in another table. There can be multiple FKs. FKs can be have duplicate & null values.

Secondary Key
Secondary key may or may not be unique field. Some times records are required to access by a field other than the primary key. In these situations another key that is used is called secondary key.
Composite Key
Composite key consists of two or more than two fields. Composite key is also designed as a primary key. It is created in a situation when no single field fulfills the property of uniqueness. To make unique more than one field are combined and used as primary key.
Constraints
SQL constraints are used to specify rules for data in a table.
- NOT NULL : columns cannot have null value. col1 INT NOT NULL
- UNIQUE : all values in column are different. col2 UNIQUE
- PRIMARY KEY : makes a column unique & not null but used only for one. id INT PRIMARY KEY. also declare as PRIMARY KEY (id).
Foreign Key
Prevent actions that would destroy links between tables.
CREATE TABLE temp(
cust_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (cust_id) references customer(id)
);
DEFAULT
sets the default value of a column
salary INT DEFAULT default_value;
CHECK
It can limit the values allowed in a column.
CREATE TABLE city(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
city VARCHAR(50),
age INT,
CONSTRAINT age_check CHECK (age>= 16 AND city="Delhi")
);
CREATE TABLE newTab (
age INT CHECK (age>=18)
);
Select in Detail
SELECT
The SELECT statement is used to select data from a database.
SELECT col1,col2 FROM table_name;
To Select All
SELECT * FROM table_name;
Tip: DISTINCT Keyword Removes duplicate rows from query results.
Syntax:
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2 FROM table_name;
Where Clause
To define some conditions
SELECT col1,col2 from table
WHERE condition(s).
SELECT * FROM student WHERE marks > 80;
SELECT * FROM student WHERE city="Multan";
Operator in WHERE
- Arithmetic Operators : + , - , * , / , %
- Comparison Operators : = , != , > , >= , < , <=
- Logical Operators : AND, OR, NOT, IN, BETWEEN, ALL, LIKE, ANY
- Bitwise Operators : & , |
Operators
- AND (to check for both conditions to be true)
SELECT * FROM student WHERE marks > 80 AND city="Multan";
- OR (to check for one of the conditions to be true)
SELECT * FROM student WHERE marks > 90 OR city="Lahore";
- BETWEEN : select for a given range
SELECT * FROM student WHERE marks BETWEEN 80 AND 90;
- IN : (matches any value in the list)
SELECT * FROM student WHERE city IN ("Multan","Karachi")
- NOT : (to negate the given condition)
SELECT * FROM student WHERE city NOT IN ("Multan", "Karachi")
Limit Clause
The limit clause is used to sets an upper limit on number of(tuples)rows to be returned.
SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 3;
SELECT col1,col2 FROM table_name
LIMIT number;
Order by Clause
To sort in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order.
SELECT * FROM student ORDER BY city ASC;
SELECT col1,col2 FROM table_name ORDER BY col_name(s) ASC;
Aggregate Functions
Aggregate functions perform a calculation on a set of values, and return a single value.
- COUNT()
- MAX()
- MIN()
- SUM()
- AVG()
Get Maximum Marks
SELECT MAX(marks) FROM student;
Get Average marks
SELECT AVG(marks) FROM student;
Group By Clause
Group rows that have the same values into summary rows. It collect data from multiple records(rows) and groups the result by one ore more column.
Generally we use the group by with some aggregation function.
Count number of students in each city
SELECT city, count(name)
FROM student
GROUP BY city;
HAVING Clause
Similar to WHERE i.e., applies some condition on rows. Used when we want to apply any condition after grouping.
Count number of students in each city where max marks cross 90.
SELECT city, count(rollno)
FROM student
GROUP BY city
HAVING MAX(marks) > 90;
General Order
SELECT column(s) FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column(s) HAVING condition ORDER BY column(s) ASC;
Example:
SELECT city
FROM student
WHERE grade = "A"
GROUP BY city
HAVING MAX(marks) > 90
ORDER BY city DESC;
Table related Queries
UPDATE is used to update existing rows in a table.
UPDATE table_name
SET col1=val1, col2=val2
WHERE condition;
UPDATE student
SET grade = "O"
WHERE grade = "A";
DELETE is used to delete the existing rows in a table
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
DELETE FROM student
WHERE marks < 33;
Foreign Key
A foreign key (FK) is a column or a set of columns in a table that establishes a link between data in two tables. It refers to the primary key (PK) in another table, ensuring data integrity and enforcing referential constraints.
CREATE TABLE Orders (
order_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES Customers(customer_id)
);
Cascading for FK
On Delete Cascade
When we create a foreign key using this option, it deletes the referencing rows in the child table when the referenced row is deleted in the parent table which has a primary key.
On Update Cascade
When we create a foreign key using UPDATE CASCADE the referencing rows are updated in the child table when the referenced row is updated in the parent table which has a primary key.
CREATE TABLE teacher(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
dept_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (dept_id) references dept(id)
ON UPDATE CASCADE
ON DELETE CASCADE
);
Alter
The ALTER is used to change the schema of table in a database.
- ADD Column
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD COLUMN column_name datatype constraint;
- DROP Column
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name;
- RENAME Column
ALTER TABLE table_name
RENAME TO new_table_name;
- CHANGE Column(rename)
ALTER TABLE table_name
CHANGE COLUMN old_name new_name new_datatype new_constraint;
- MODIFY Column(modify datatype/ constraint)
ALTER TABLE table_name
MODIFY col_name new_datatype new_constraint;
Truncate
The TRUNCATE is used to delete the data of table in database.
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name ;
Joins in SQL
JOIN is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
1. Inner Join
Returns records that have matching values in both tables
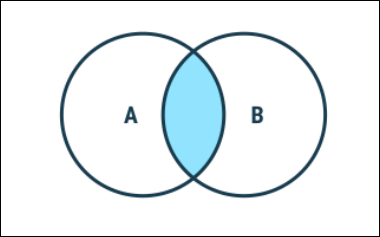 Syntax
Syntax
SELECT column(s)
FROM tableA
INNER JOIN tableB
ON tableA.col_name = tableB.col_name;
Example
SELECT *
FROM student
INNER JOIN course
ON student.student_id = course.student_id;
Tip: SQL aliases are used to give a table, or a column in a table, a temporary name. Aliases are often used to make column names more readable. An alias only exists for the duration of that query. An alias is created with the AS keyword.
SELECT CustomerID AS ID
FROM Customers;
2. Left Join
Returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table.
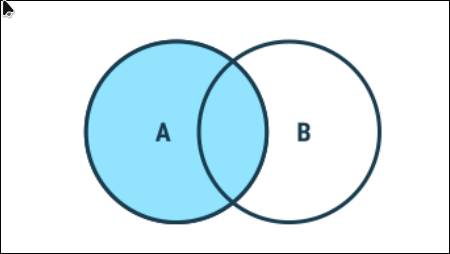 Syntax
Syntax
SELECT columns(s)
FROM talbeA
LEFT JOIN tableB
ON tableA.col_name = tableB.col_name;
Example
SELECT *
FROM student as s
LEFT JOIN course as c
ON s.student_id = c.student_id;
3. Right Join
Returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table
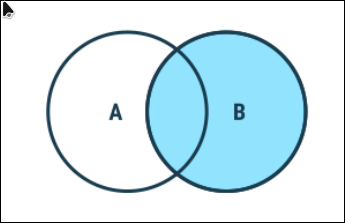
Syntax
SELECT column(s)
FROM tableA
RIGHT JOIN tableB
ON tableA.col_name = tableB.col_name;
Example
SELECT *
FROM student as s
RIGHT JOIN course as c
ON s.student_id = c.student_id;
4. Full Join
Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table

SELECT * FROM student AS s
LEFT JOIN course AS c
ON s.student_id = c.student_id
UNION
SELECT * FROM student AS s
LEFT JOIN course AS c
ON s.student_id = c.student_id;
Left Exclusive Join
Exclusive joins in SQL are used to retrieve records that exist in one table but not in the other when performing a LEFT JOIN or RIGHT JOIN.
A Left Exclusive Join retrieves records from the left table that do not have matching records in the right table.
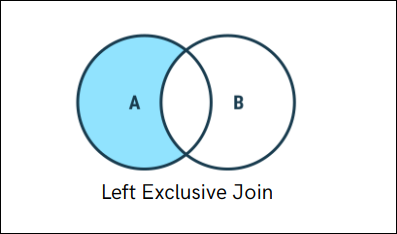
SELECT *
FROM student AS a
LEFT JOIN course AS b
ON a.id = b.id
WHERE b.id IS NULL;
Right Exclusive Join
A Right Exclusive Join retrieves records from the right table that do not have matching records in the left table.
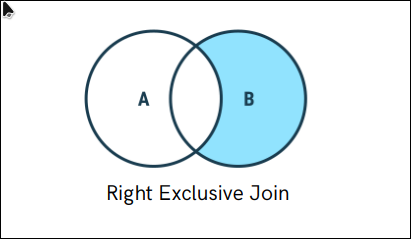
SELECT *
FROM student AS a
RIGHT JOIN course AS b
ON a.id = b.id
WHERE a.id IS NULL;
Self Join
It is a regular join but the table is joined with itself.
SELECT column(s)
FROM table as a
JOIN table as b
ON a.col_name = b.col_name
Union
It is used to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements. Gives UNIQUE records.
- every SELECT should have same no. of columns
- columns must have similar data types
- columns in every SELECT should be in same order
SELECT column(s) FROM tableA
UNION
SELECT column(s) FROM tableB
and we can also use the UNION ALL to give all the values including the duplicates records.
SQL Sub Queries
A Subquery or Inner query or a Nested query is a query within another SQL query. It is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition.
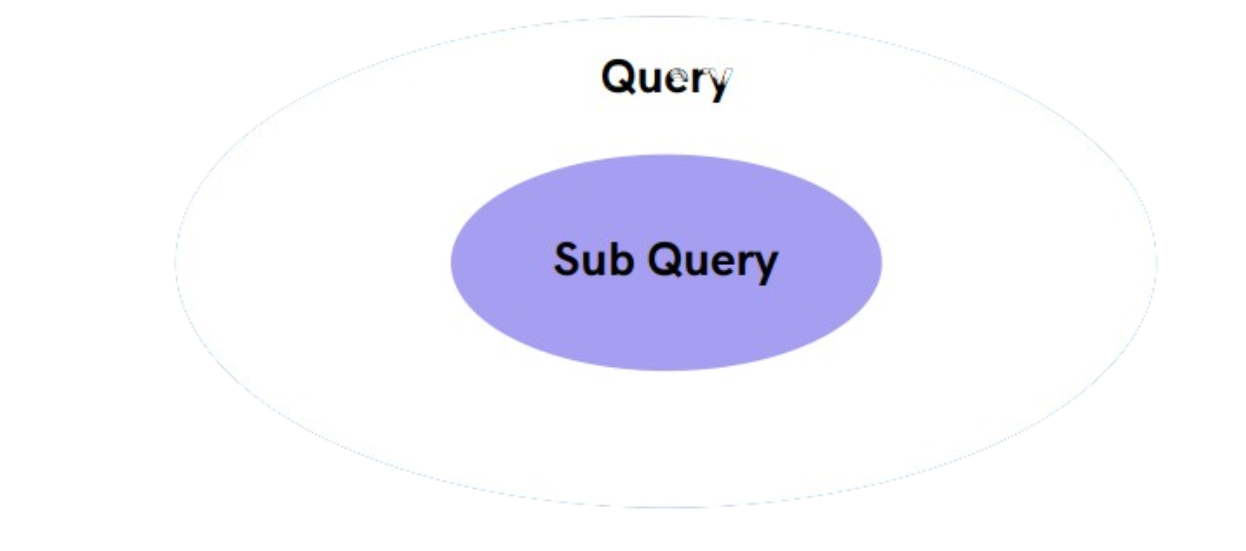
It involves 2 select statements.
Syntax
SELECT column(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE col_name operator
( subquery );
Example with FROM
SELECT MAX(marks)
FROM (SELECT marks FROM student WHERE city = 'Delhi') AS temp;
MySQL Views
A view is a virtual table based on the result-set of an SQL statement.
A view always shows up-to-date data. The database engine recreates the view, every time a user queries it.
CREATE VIEW v1 AS
SELECT rollno, name, marks
FROM student;
Stored Procedures in MySQL
A Stored Procedure is a precompiled set of SQL statements stored in the database that can be executed repeatedly. It helps encapsulate logic in a modular way, improving reusability, maintainability, and performance.
Benefits of Stored Procedures
- Modularity – Write once, use many times.
- Performance – Precompiled for faster execution.
- Security – Users can be granted access to run procedures without giving access to underlying tables.
- Reduced network traffic – Fewer queries sent between application and server.
Syntax: Creating a Stored Procedure
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name (
IN param1 datatype,
OUT param2 datatype,
INOUT param3 datatype
)
BEGIN
-- SQL statements go here
END //
DELIMITER ;
Example:
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE GetEmployeeByID(IN emp_id INT)
BEGIN
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE id = emp_id;
END //
DELIMITER ;
Calling a Stored Procedure
CALL GetEmployeeByID(1);
If there are OUT or INOUT parameters:
CALL ProcedureName(@out_param);
SELECT @out_param;
Types of Parameters
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
IN | Input only (passed by value). |
OUT | Output only (value returned). |
INOUT | Both input and output (passed by reference). |
Modifying or Dropping Stored Procedures
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS procedure_name;
- Alter is not supported: You must drop and recreate the procedure.
Control Structures in Stored Procedures
IF-ELSE
Used to execute different blocks of code based on a condition.
IF condition THEN
-- statements
ELSE
-- statements
END IF;
Example:
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE CheckAge(IN age INT)
BEGIN
IF age >= 18 THEN
SELECT 'You are an adult' AS result;
ELSE
SELECT 'You are a minor' AS result;
END IF;
END //
DELIMITER ;
-- Call the procedure
CALL CheckAge(20); -- Output: You are an adult
CALL CheckAge(15); -- Output: You are a minor
CASE Statement
Used as an alternative to multiple IF statements when checking several conditions.
Syntax:
CASE variable
WHEN value1 THEN statement1;
WHEN value2 THEN statement2;
ELSE statement_default;
END CASE;
Example:
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE GradeResult(IN grade CHAR(1))
BEGIN
CASE grade
WHEN 'A' THEN SELECT 'Excellent' AS Result;
WHEN 'B' THEN SELECT 'Good' AS Result;
WHEN 'C' THEN SELECT 'Average' AS Result;
ELSE SELECT 'Fail or Invalid Grade' AS Result;
END CASE;
END //
DELIMITER ;
-- Call the procedure
CALL GradeResult('A'); -- Output: Excellent
CALL GradeResult('D'); -- Output: Fail or Invalid Grade
WHILE Loop
Repeats a block of statements while the condition is true.
Syntax
WHILE condition DO
-- statements
END WHILE;
Example:
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE CountToFive()
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1;
WHILE i <= 5 DO
SELECT CONCAT('Count: ', i) AS Output;
SET i = i + 1;
END WHILE;
END //
DELIMITER ;
-- Call the procedure
CALL CountToFive();
## REPEAT Loop
Similar to WHILE, but checks the condition after executing the block.
Syntax:
REPEAT
-- statements
UNTIL condition
END REPEAT;
Example:
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE RepeatExample()
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1;
REPEAT
SELECT CONCAT('Repeat Count: ', i) AS Output;
SET i = i + 1;
UNTIL i > 5
END REPEAT;
END //
DELIMITER ;
-- Call the procedure
CALL RepeatExample();
Error Handling
Use DECLARE ... HANDLER to define how to handle errors.
Syntax
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR SQLEXCEPTION
BEGIN
-- Error handling code
END;
Create the procedure with error handler
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE InsertStudent (
IN student_id INT,
IN student_name VARCHAR(50)
)
BEGIN
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR SQLEXCEPTION
BEGIN
SELECT 'Error occurred while inserting student!' AS ErrorMessage;
END;
-- Attempt to insert student
INSERT INTO students (id, name) VALUES (student_id, student_name);
-- Continue execution even if error occurred
SELECT 'Insert attempt completed.' AS Status;
END //
DELIMITER ;
Show Existing Stored Procedures
SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS WHERE Db = 'your_database';
Or to view the code:
SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name;